Emergency Use of Medical Oxygen 101
₨10,000.00
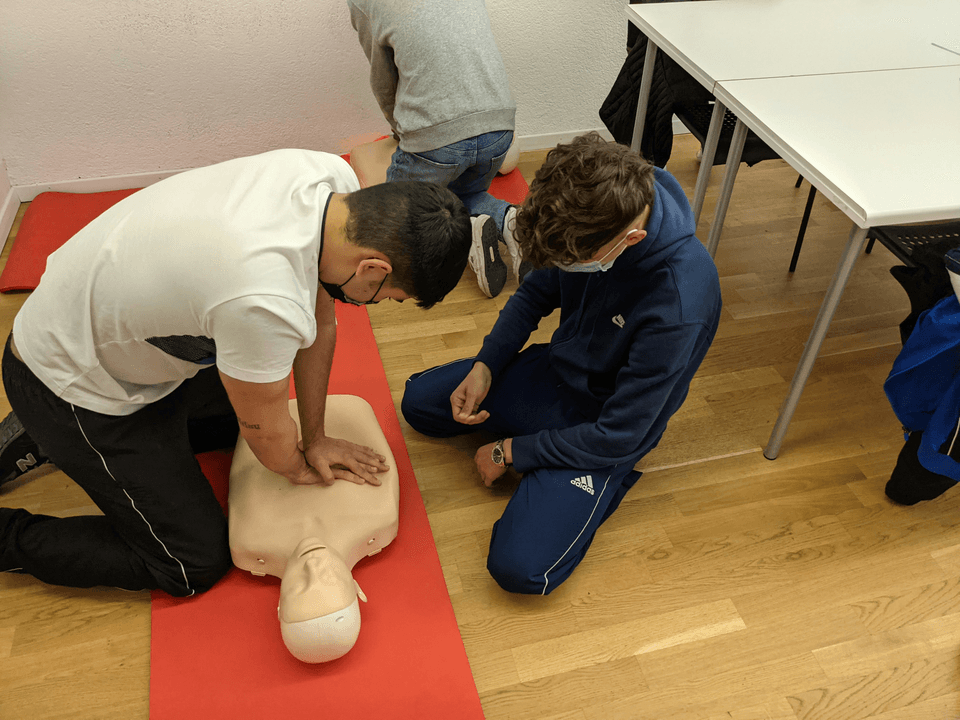
Participants will learn the fundamentals of oxygen physiology, indications for oxygen use, equipment handling, and safety precautions. The course emphasizes hands-on practice and real-world scenarios to build confidence in emergency oxygen administration across healthcare, workplace, and community settings.
This course is suitable for healthcare professionals, first responders, safety officers, workplace emergency teams, and trained first aiders, supporting improved patient outcomes during respiratory and cardiac emergencies.
Emergency Use of Medical Oxygen 101

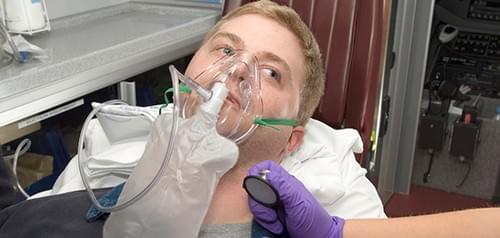
Why Do We Need Emergency Oxygen?
The air a person normally breathes contains approximately 21% oxygen. The concentration of oxygen delivered to a victim through rescue breathing is 16%. A condition known as hypoxia (insufficient oxygen to the body) can occur if a person goes without adequate oxygen for an extended period.
When Should Emergency Oxygen Be Used?
You should provide medical oxygen to a victim having difficulty breathing if it is available and if you are trained to administer oxygen. Medical oxygen should be considered if the person is showing signs and symptoms of hypoxia or if a pulse oximeter reading is 94% or lower.
Never delay appropriate care for life-threatening conditions, such as CPR, AED, or control of severe bleeding to get, set up, or administer medical oxygen in an emergency.
Signs and Symptoms of Hypoxia
Never withhold medical oxygen in an emergency when a person has signs and symptoms of hypoxia, with or without a pulse oximeter.
Mild Hypoxia
- SpO2 reading of 91%-94%
- Anxiety, confusion, restlessness
Moderate Hypoxia
- SpO2 reading of 86%-90%
- Rapid breathing
- Flaring of nostrils or pursed lips
- Rapid or slow heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Wheezing
- When breathing in, the person’s skin may suck in around and between the ribs or above the breastbone.
- The person may lean over by resting arms on their legs to increase lung expansion.
- The person may be unable to speak in full sentences or may need to catch their breath between sentences.
Severe Hypoxia
- SpO2 reading of 85% or less
- Changes in skin appearance and condition, such as sweaty, cool skin, and blue-tinged nail beds and lips.
- In people with darker skin pigmentation, the blue tinge may be more noticeable in the tissue that lines the inside of the eyelids and lips.
- The person may have an altered mental status or become unresponsive.



